The luck of the Irish was with USS O’Bannon (DD 450) not once, but many times during the perilous years of World War II. The ship was named for First Lieutenant Presley Neville O’Bannon, a hero during the Barbary War who became a U.S. Marine Corps legend.
His namesake would also become legendary when a staple of the Emerald Isle’s diet unexpectedly came in handy during an encounter with a Japanese submarine in 1944.
O’Bannon, like the man it was named after, was impressive. The Fletcher-class destroyer, launched in 1942, could move at 35 knots and had more than 140 guns, torpedo tubes, and six depth charge tracks. Its first mission upon entering the war was to fight in the Guadalcanal Operation.
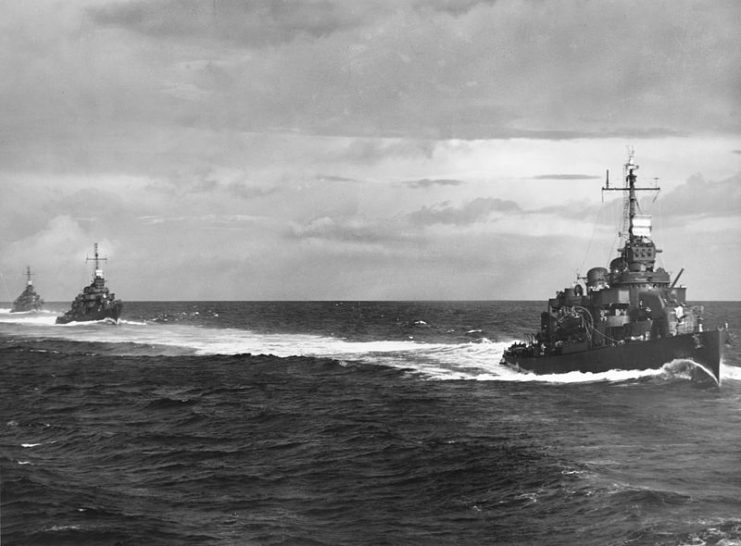

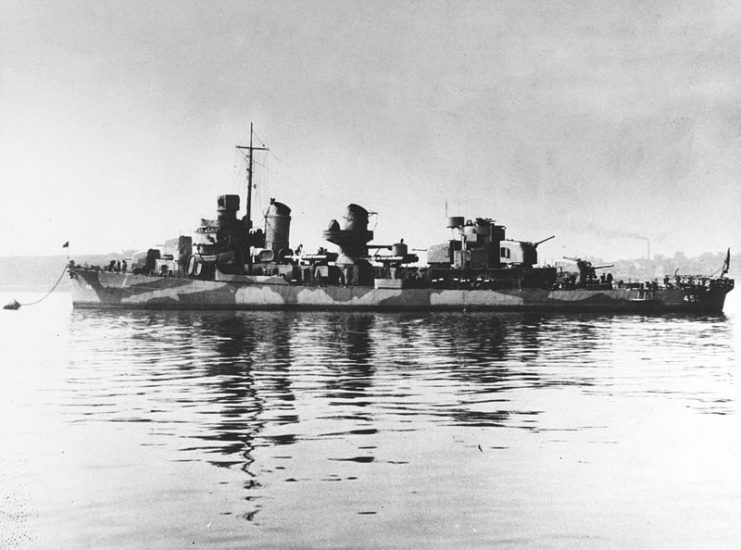
The U.S. had numerous fronts to defend and not enough resources, so O’Bannon was sent to New Caledonia. There, it partnered with the 21st Destroyer Squadron, and together they escorted other ships filled with reinforcements for campaigns throughout the Pacific.
https://youtu.be/MqllihZqzf4
The Americans and Japanese clashed on August 7, 1942, at the Solomon Islands. Previously, the Japanese had lost an important airfield, Runga Point, to the Americans, who renamed it Henderson. The Japanese wanted the airfield back, but failing that, they wanted to destroy it. The Japanese knew the airfield was vital to American operations in the South Pacific.
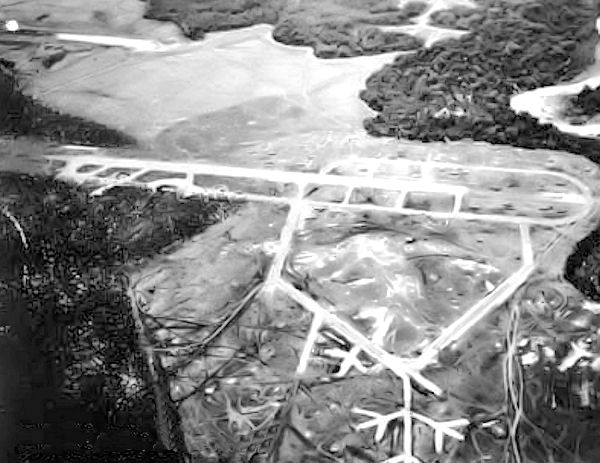



Twenty-four hours after their arrival in the area, the Japanese descended with 14 destroyers, two battleships and a light cruiser.
The U.S. was out-manned and out-gunned. One of the Japanese battleships, Hiei, was a massive bruiser double the size of O’Bannon, and heavily armed. As soon as the Americans saw it, they attacked.



O’Bannon had speed on its side, and it rode lower in the sea than Hiei. It sped alongside and fired repeatedly, so close that all the Japanese could do was fire over the heads of O’Bannon‘s crew. They crippled Hiei quickly, and American planes swooped in and promptly finished the job. Finally, the remaining Japanese ships had to pull back to regroup.
O’Bannon would again encounter the considerable force of the Japanese Imperial Navy two years after its victory over Hiei. But this time, it wasn’t a battleship they fought.
RO-34 was a Kaichū VI type medium sized submarine, outfitted with both an anti-aircraft gun and an anti-aircraft machine gun. One night in 1944, it was surfaced on the South Pacific when O’Bannon caught sight of it and decided to act.
Initially, O’Bannon intended to ram the sub. It accordingly charged ahead, but changed course at the last second when the crew realized the sub might be a mine layer. A collision would have meant disaster for the American crew, not only the Japanese.

O’Bannon veered so sharply to avoid the collision that it was now suddenly right alongside RO-34. In a reversal of fortune of the Hiei incident, O’Bannon was too close to fire upon the sub, but RO-34 was well able to fire at O’Bannon.
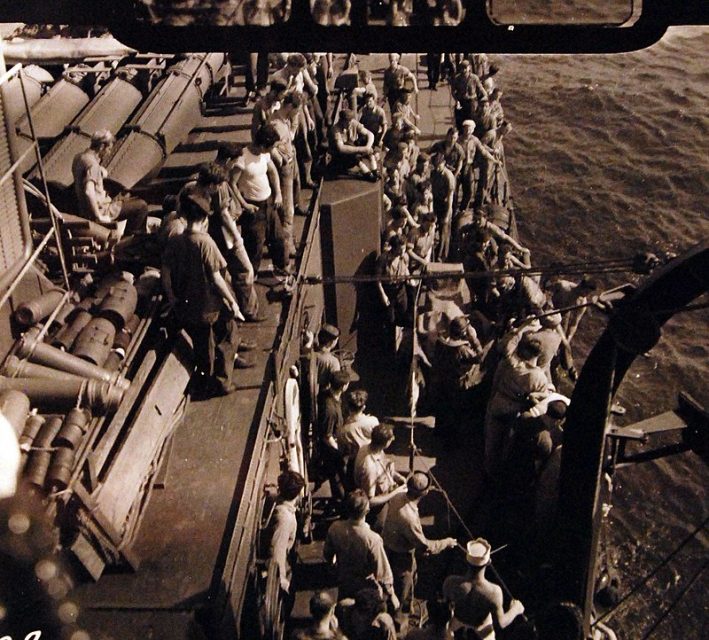
Lacking side arms, the crew of O’Bannon began pitching the only weapon at their disposal – potatoes – at the Japanese crew topside.
The Japanese panicked, as they mistakenly but rather understandingly thought the flying objects were hand grenades. Many of them either threw the potatoes back at the Americans, or tossed them into the sea.
This spontaneous, clever action bought time for O’Bannon to put a safe distance between itself and RO-34.
Once it had gained enough distance from the sub, O’Bannon began firing, and sank RO-34. Furthermore, the American ship took out two enemy planes later that day as well.
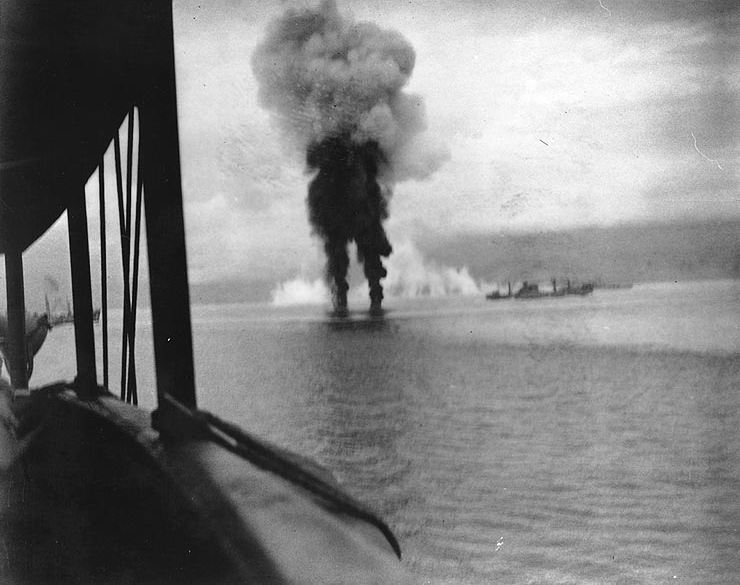

O’Bannon undertook many more battles in World War II, and became the most decorated destroyer during the war. It received 17 battle stars and a Presidential Citation. It also received an honor unlike any other: a commemorative plaque from the Maine Association of Potato Growers. The incident became known as the “Maine Potato Episode.”

The crew of O’Bannon were rightly lauded for their quick thinking and cool heads under pressure, but clearly, their ship had something else on its side: the enduring and fabled luck of the Irish.
