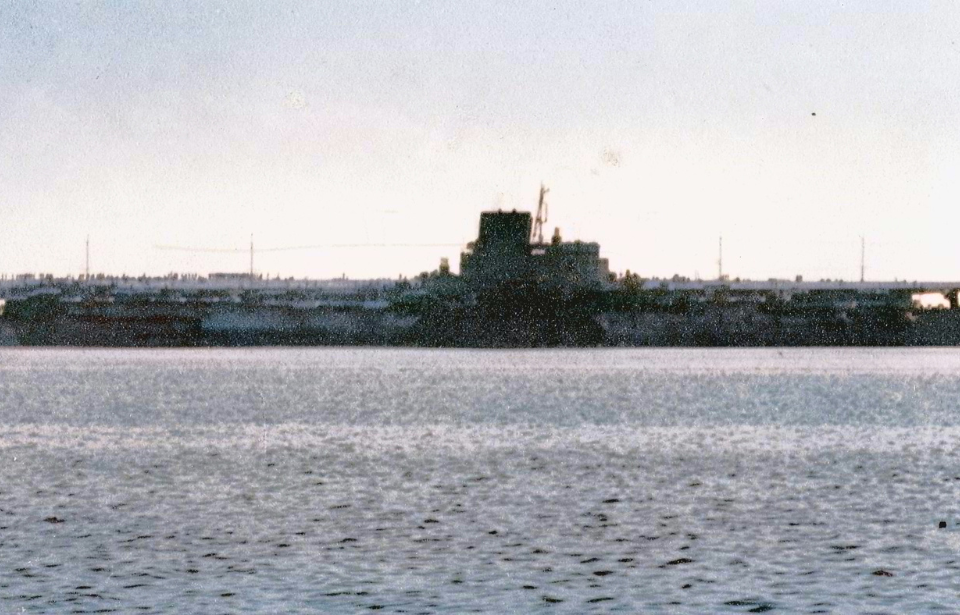
During World War II, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) constructed several notable warships, with the IJN Shinano standing out as particularly famous. Initially intended to be a Yamato-class battleship, strategic adjustments after the Japanese fleet’s losses at the Battle of Midway led to its conversion into an aircraft carrier.
Shinano is historically important as it was the largest warship ever sunk by a submarine attack.
Construction of the IJN Shinano
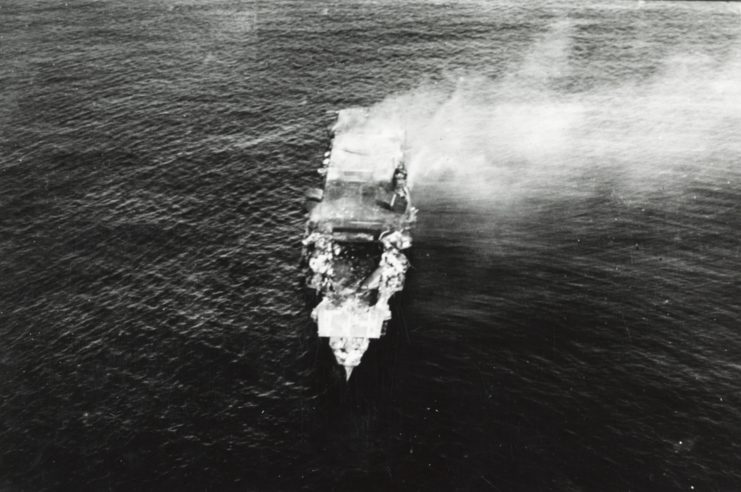

Construction of the IJN Shinano began on May 4, 1940, at the Yokosuka Naval Arsenal and progressed smoothly until 1942. However, that year, a series of strategic defeats by the Americans necessitated her conversion from a battleship to an aircraft carrier. Rather than becoming a fleet carrier, Shinano was reconfigured as a heavily-armored support carrier with a displacement of 65,800 tons, primarily designed to store reserve aircraft and fuel.
Shinano‘s construction was conducted under a veil of secrecy, with a high fence erected around the site to prevent any public visibility. Workers were bound by strict confidentiality agreements, with severe penalties, including execution, for any breaches.
As a result, Shinano stands as the only major warship of the 20th century with no known construction photographs. Even after completion, it was only captured on film twice: once by a Boeing B-29 Superfortress during a reconnaissance mission and once by a civilian during sea trials.
Armor and armament

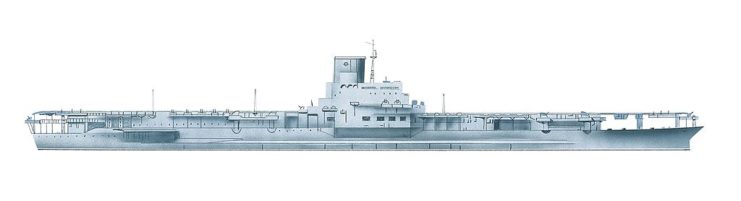
The IJN Shinano underwent modifications influenced by the design of the design of the Yamato and Musashi. Originally planned to have slightly thinner armor by 10-20 mm and fitted with newer anti-aircraft guns, these specifications were altered when she was repurposed into an aircraft carrier. Consequently, Shinano diverged significantly from the typical appearance of a Yamato-class ship, shedding a considerable portion of her armor and large main guns.
In her new form, Shinano took on the characteristic flat top of aircraft carriers and a streamlined flight deck.
Shinano boasted impressive dimensions, measuring 872 feet in length, with a beam of 119 feet and a draught of nearly 34 feet. Her power source consisted of 12 Kampon water boilers, driving four geared steam turbines, which in turn propelled an equal number of shafts, producing 150,000 shaft horsepower. Under optimal conditions, this setup enabled the aircraft carrier to achieve a surface speed of approximately 27-28 knots.
Traveling toward certain destruction

Initially slated for commissioning in early 1945, the construction scheduled for the IJN Shinano was expedited following the Battle of the Philippine Sea. The engagement inflicted major losses on the Japanese Navy, including two fleet carriers, one light carrier and two oilers, with several smaller vessels sustaining damage.
The accelerated construction of Shinano resulted in compromised workmanship on later components. Despite this, she was launched on October 8, 1944, and commissioned on November 19 of the same year.
Following her commissioning, Shinano was scheduled to transit from her shipyard to Kure Naval Base, where she’d be armed and receive aircraft under the command of Capt. Toshio Abe. Despite pressure from superiors to depart immediately, Abe requested a delay, due to incomplete bailing pumps and fire mains. Unfortunately, his plea was denied, and he was forced to set sail at night, contrary to his preference for a daytime departure.
Leaving at 6:00 PM on November 28, 1944, Shinano was accompanied by Isokaze, Yukikaze and Hamakaze. While en route, the ships detected radar signals that indicated the presence of an American submarine nearby, prompting them to employ evasive maneuvers. Unbeknownst to the crew, these inadvertently placed Shinano directly in the path of the USS Archerfish (SS-311).
Sinking of the IJN Shinano
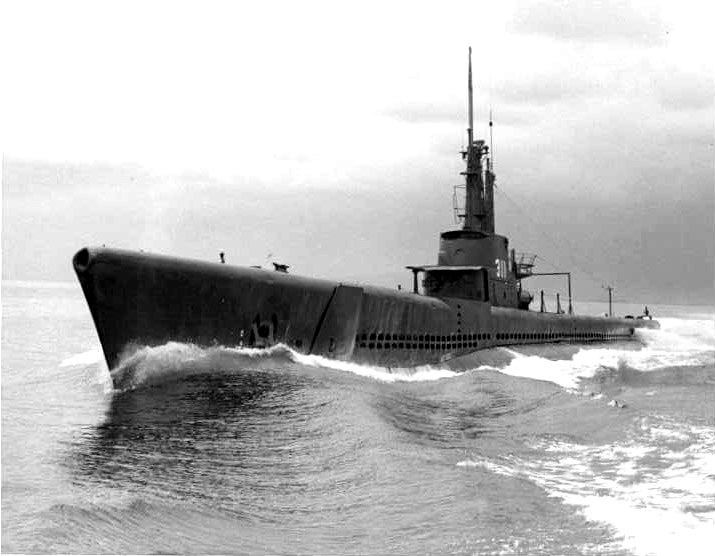

Commander Joseph Enright, commanding the USS Archerfish, detected the IJN Shinano two hours before the Japanese aircraft carrier became aware of the submarine’s presence. Believing the submarine to be part of an American wolfpack, Commander Abe of the Japanese forces ordered his ships to change course to evade the Archerfish. Despite the Shinano being faster, she had to slow down to avoid potential damage.
At 2:56 AM on November 29, Abe initially steered towards the submarine but then veered southwest, inadvertently exposing the Shinano’s entire flank to the Archerfish. At 3:15 AM, Enright gave the command to fire six torpedoes, two of which found their mark before the submarine dived to a depth of 400 feet to avoid retaliation.
The Shinano was struck by four torpedoes, causing her to sink. Enright and his crew remained unaware of the carrier’s identity until the end of the Second World War, unaware that it took over seven hours for the Shinano to sink after being hit.
Hindsight is 20/20
Initially, those aboard the IJN Shinano underestimated the severity of the damage caused by the torpedo strikes, meaning minimal effort was made to salvage the ship. Abe, in particular, directed her to maintain maximum speed, inadvertently accelerating the flooding of the aircraft carrier.
Unfortunately, by the time they grasped the gravity of the situation, it was too late. The ship had become too heavy to be towed by escort vessels, too inundated to be pumped out and too irreparably damaged for the majority of her crew to evacuate. Out of her 2,400-man crew, 1,435 perished with the ship, including Abe and both navigators.
The survivors were sent to Mitsukejima until January of the subsequent year, preventing the widespread dissemination of news about Shinano‘s sinking. Following the conclusion of the war, the US Navy analyzed the aircraft carrier, along with other Yamato-class ships, and identified significant design flaws that rendered specific joints susceptible to leakage. It was concluded that the torpedoes from the USS Archerfish happened to strike these vulnerable joints, contributing to Shinano‘s demise.
Are you a fan of all things ships and submarines? If so, subscribe to our Daily Warships newsletter!
Regarding Enright, US Naval Intelligence initially doubted his claim of sinking a Japanese carrier, believing all had been identified. However, this was rectified after the war, and Enright was duly honored with the Navy Cross for his victorious achievement.
