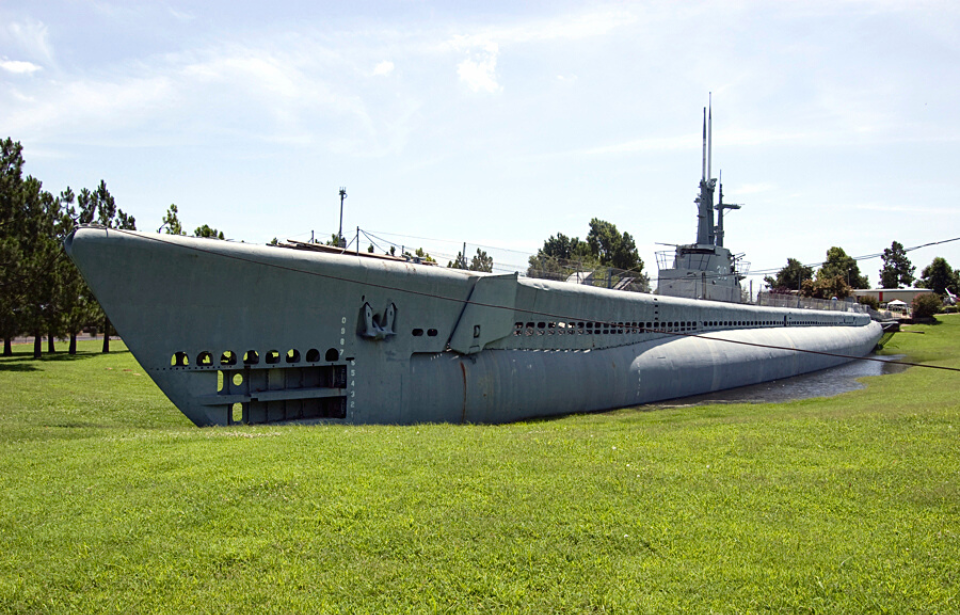
The USS Batfish (SS-310), a Balao-class submarine, made history by sinking three enemy ships in as many days, setting a record for the US Navy. Following her active duty, the vessel was decommissioned and later acquired by a committed group of veterans in Oklahoma. Their objective: transform Batfish into a memorial and museum, preserving her legacy for generations to come.
The USS Batfish enters the Second World War
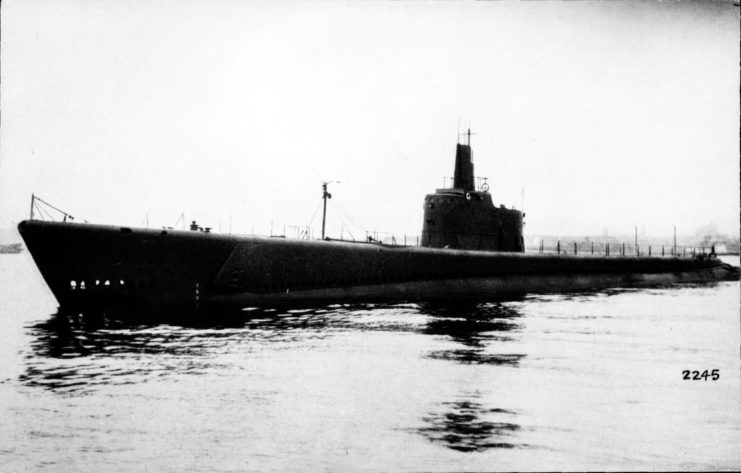

Two years after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, the USS Batfish undertook her first patrol. On January 19, 1944, the vessel experienced her first naval engagement, encountering an enemy convoy consisting of six ships. Batfish distinguished herself by sinking two of the larger vessels, initiating a battle record that earned her the moniker, “Sub Killer.”
Equipped with 10 torpedo tubes and numerous on-deck guns, Batfish proved to be a formidable submarine. During her fourth war patrol, she inflicted severe damage on the Japanese destroyer Samidare, rendering her unsalvageable. Consequently, the enemy opted to destroy the ship using demolition charges.
In total, Batfish launched 71 torpedoes during combat, with 24 successfully hitting their intended targets.
The USS Batfish sets a US Navy record
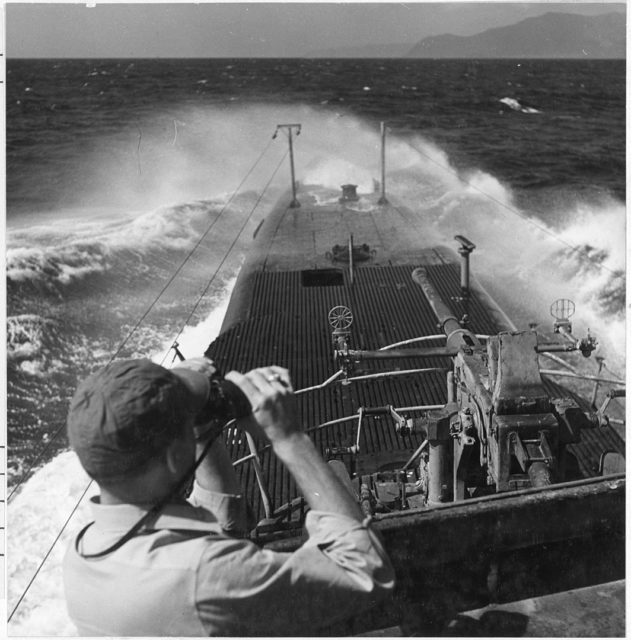

On her sixth patrol, the USS Batfish achieved a historic naval record. On February 10, 1944, she successfully sank the Japanese submarine Ro-55, just minutes after midnight. The following day, Cmdr. John Kerr Fyfe detected another enemy vessel on the radar and launched four torpedoes, three of which struck and sunk the Ro-112. Not even 24 hours later, Batfish sank the Ro-113 using three more torpedoes.
To this day, Batfish stands as the only submarine in US history to sink three enemy ships within 76 hours. Between 1943-45, her crew of 80 sunk 14 Japanese vessels and damaged an additional three. Following the Japanese surrender, the submarine was decommissioned and repurposed as a training vessel. Reactivated and later deactivated during the Korean War, she was struck from the Naval Vessel Registry in 1969.
In recognition of their extraordinary efforts, Batfish‘s crew was honored with 10 Bronze Star Medals, nine Battle Stars, four Silver Stars, one Navy Cross and one Presidential Unit Citation.
Veterans search for the right submarine
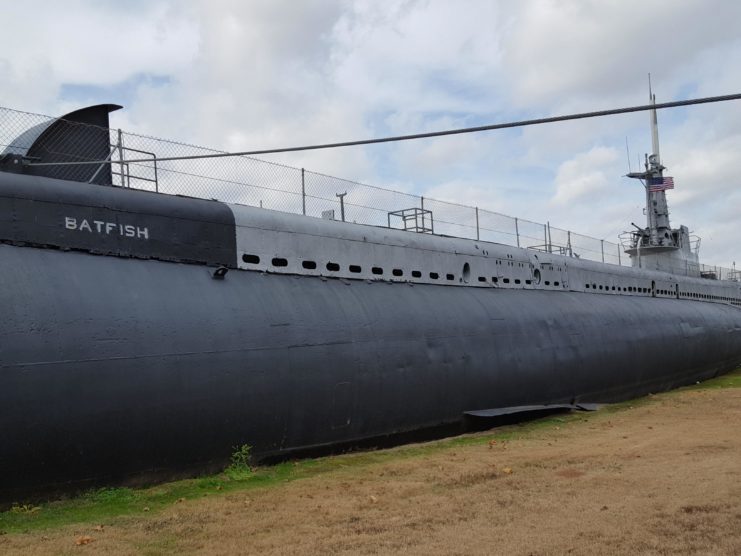

As early as 1962, the Oklahoma chapter of United States Submarine Veterans, Inc. began their quest to find a submarine suitable for preservation and transformation into a memorial. Numerous candidates were considered, each with their own storied history.
The USS Piranha (SS-389) proudly earned five battle stars and completed six combat patrols, while the USS Sea Dog (SS-401) undertook five. The USS Cavalla (SS-244), notable for sinking the Japanese aircraft carrier Shōkaku during the Pearl Harbor attack, was also in contention.
Ultimately, the veterans selected the USS Batfish, based on jer remarkable battle record and condition at the time. Piranha and Sea Dog were eventually scrapped, and Cavalla found a new life as a museum at Seawolf Park in Galveston, Texas.
Upon announcing Batfish as their chosen memorial, US Congress promptly approved the transfer of the submarine from the Navy to Oklahoma.
Moving the USS Batfish to a soybean field
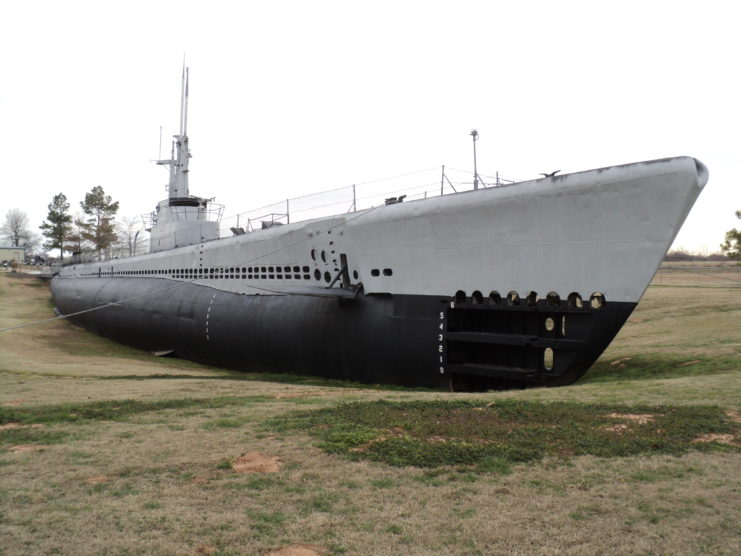

The Muskogee City-County Trust Port Authority generously allocated approximately five acres of former riverfront soybean fields to host the USS Batfish‘s exhibition space. The next hurdle was transporting the submarine from her New Orleans port to the Port of Muskogee.
This undertaking proved daunting, requiring nearly seven weeks to move Batfish from New Orleans to Oklahoma. The submarine was towed up the Mississippi River and needed the water level to be dropped by three feet to pass under a bridge. Upon reaching the Arkansas River, Batfish was moored near the designated site until a flooding incident prompted her relocation.
Once the floodwaters receded, Batfish was officially positioned and readied to welcome the public.
The USS Batfish becomes a museum

On Memorial Day 1973, the USS Batfish memorial and a neighboring museum were opened to the public. The submarine was restored by the veterans and volunteers, who reinstalled as much as they could, down to the last detail. They even hung pin-up girl posters on the walls for full authenticity.
Want War History Online‘s content sent directly to your inbox? Sign up for our newsletter here!
By the end of the 20th century, Batfish was one of 20 World War II-era submarines on public display in the United States.