The sabot round is a form of tank ammunition crafted specifically for armored warfare. This non-explosive, anti-tank round delivers a projectile that hits its target with precision and tremendous force. On impact, the chance of survival for the enemy tank crew is minimal, making the sabot round a popular option in combat.
Inner workings of the Sabot round

The sabot round is designed to attach a smaller projectile to the tank’s barrel, allowing the propellant gases to work across a larger area instead of just the projectile itself. This setup lets the round reach a high muzzle velocity, even if its aerodynamics aren’t fully optimized for the barrel’s internal ballistics.
The sabot encases and stabilizes the projectile as it moves through the barrel. Once it leaves the muzzle, the sabot falls away, enabling the projectile to speed toward its target—often reaching velocities close to 3,500 MPH.
The projectile is generally made of a depleted uranium rod intended for piercing armor. On impact, it shatters into a spray of metal fragments, causing destruction so severe that one soldier described it as “liquefying” everything and everyone inside the struck tank or armored vehicle.
Different types of sabot rounds
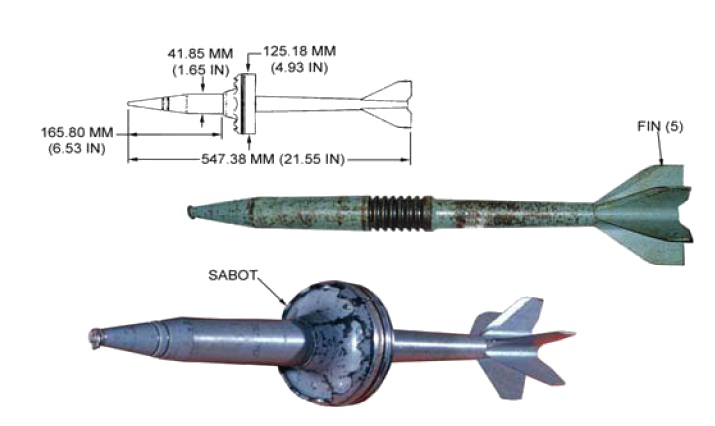
There are five different types of sabot rounds. The cup sabot supports the base of the projectile and offers structural support around the shaft. It’s typically used in small arms ammunition, as well as smoothbore shotgun and muzzleloader projectiles.
The expanding cup sabot is similar to the cup round, in that it’s used for rifled small arms. However, when fired, the centrifugal force from the rotation of the projectile causes the segments surrounding it to open up. This introduces more surface area to the surrounding air pressure, releasing it.
The base sabot has a one-piece base that supports the bottom of the projectile, as well as separate pieces that surround the sides and center, breaking away once the round has been fired. This sabot is considered superior to the previous two, as it offers a cleaner and better sabot-projectile separation. However, it’s more expensive to produce.
The spindle sabot is typically used in large caliber armor-piercing ammunition. It uses between two and four longitudinal rings with a center section that makes contact with the projectile. The front centers the projectile in the barrel and provides an air scoop to help with its separation from the sabot, while the rear seals the propellant gases with an obturator ring along the outside diameter.
Finally, the ring sabot uses the projectile’s rear fins to center it, forming a single ring around the front with an obturator ring to seal the gases. This type of sabot was favored by the Soviet Union, as the steel from which it was constructed could withstand launch accelerations without needing a ramp to support the projectiles.
Multiple generations of sabot round munitions

The M829A1, known as the “Silver Bullet,” is an armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) round. It has a long-rod, uranium-depleted projectile that’s about 1.25 inches wide. Once it hits its target, it punches through armor and typically explodes an enemy tank in what tankers call a “jack in the box” effect.
According to Sofrep, the M829A1 “is widely regarded as the most effective tank-fired (M1 Abrams 120mm main gun) anti-armor weapons in the world. It overwhelmed Iraqi armor during Operation Desert Storm. The M829A1 is a depleted-uranium long-rod kinetic energy penetrator round capable of defeating heavily armored vehicles.”
Since then, multiple generations of the round have been developed. The M829A2 improved the structural quality of the uranium-depleted projectile, while the M829A3 made the propellant more efficient to boost muzzle velocity. The M829A4 uses a uranium-depleted projectile with a three-petal composite sabot.
Use during Operation Desert Storm

More from us: 5.56 vs 7.62: Which is the Better Long Distance Round?
Want to become a trivia master? Sign up for our War History Fact of the Day newsletter!
The M1A2 Abrams tank was used throughout Operation Desert Storm and fired 120 mm M829 sabot rounds at enemy armored vehicles; the projectiles took out multiple tanks as they dominated the battlefield. M829 sabot rounds are best used in armored warfare, rather than toward buildings or walls, so were thoroughly employed by the US military throughout the Gulf War.
